LCDs are present everywhere from small hand devices to computer monitors to large billboards on the roadside or shopping centers.
Before the invention of the LCD, we had used cathode ray tube displays in TV sets, which used an electron gun that shot the electron to the phosphor coating to the inner side of the screen. In 1980 LCD started replacing CRT TVs and displays.
Plasma displays were once popular along with the LCD But after that, they disappeared soon because low-cost LCDs were available in the more efficient market, run on less electricity, and produce good brightness and picture quality.
The plasma displays have used gasses like Neon and Xenon that are filled in the hair-thin glass tube which is difficult and costly to manufacture.
However, the LCDs are good for the displays of all kinds of devices. It is also used in smartphones, monitors, TVs, and other kinds of gadgets that require a display.
However, this technology has become popular in premium smartphones and TV screens.
History of OLED Display
The history of OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays is a fascinating journey of scientific innovation and technological advancement. It all began in the mid-20th century, with researchers exploring the potential of organic materials to emit light when subjected to an electric current. This foundational work set the stage for future breakthroughs.
A significant milestone came in 1987 when Ching W. Tang and Steven Van Slyke at Eastman Kodak created the first practical OLED device. Their pioneering work demonstrated that OLEDs could be efficient enough for use in display technology, offering the promise of thinner, more flexible, and energy-efficient screens compared to traditional LCDs and LEDs.

The 1990s and early 2000s saw companies like Pioneer and Sony experimenting with OLED technology. In 1997, Pioneer launched the first commercial OLED display in a car stereo. This was followed by Sony’s introduction of the XEL-1 in 2007, the first OLED television. Although it was small and expensive, the XEL-1 highlighted the superior picture quality and sleek design that OLED technology could offer.
The 2010s marked a period of rapid development and commercialization, driven by major players such as Samsung and LG. These companies poured significant resources into research and production, leading to OLED displays becoming common in smartphones, televisions, and wearable devices. Samsung’s Galaxy series and LG’s OLED TVs were particularly noted for their vibrant colors, deep blacks, and wide viewing angles, setting new standards for display quality.
Today, OLED technology continues to evolve. Innovations in flexible and foldable displays are pushing the boundaries of what is possible, making devices more versatile and user-friendly. Advancements are also being made to improve the durability of OLED screens and reduce production costs, making this cutting-edge technology more accessible to a broader audience.
What is an OLED display?
OLED is the short form of Organic Light light-emitting diodes. The Organic Light Emitting materials are named because of they contain the carbon-carbon or the Carbon-hydrogen bonding in their molecules. These types of bonds are organic material and abundant in nature.
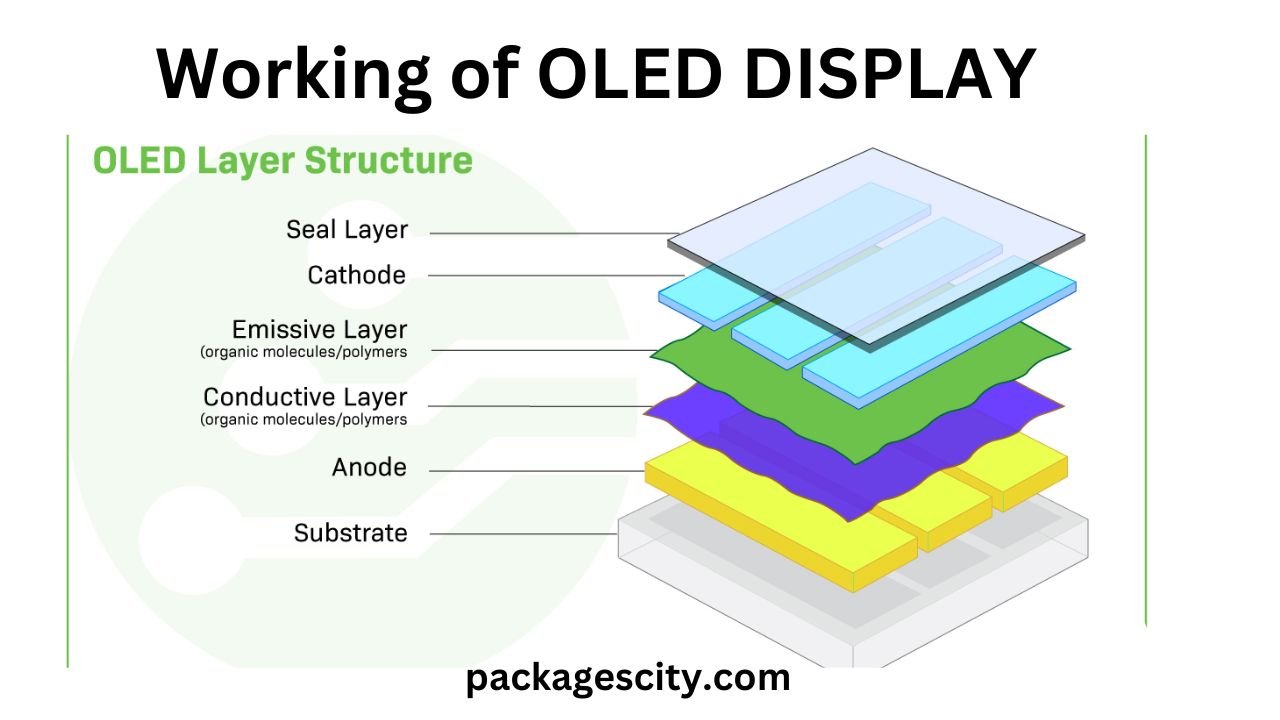
The OLED display when they are connected to a voltage source. The Pixels of the OLED TV are using this material. Before I explain the working model of the OLED display first we talk about the working of the Liquid crystal display.
LCDs use liquid crystal technology which is sandwiched between two thin layers of glass, These LCDs later allow light to pass through the screen and can be controlled using the amount of voltage applied to the liquid crystal layers. It is like a window that allows the light to pass through when the electric current is applied.
In the diagram, you can see how an LCD TV or display is made up of different thin layers. The layer which is back is called backlight which is composed of tiny emitting diodes. The verticle polarizer only allows a single polarization that light to pass through. It is made of a thin plastic-like material called PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol).
Types of OLED Displays
Passive-Matrix OLED (PMOLED)
PMOLED displays are simpler and less expensive to produce. They are suitable for smaller screens but have limitations in terms of size and resolution.
Active-Matrix OLED (AMOLED)
AMOLED displays, on the other hand, offer higher resolution and are used in larger, more complex screens. They incorporate a thin-film transistor (TFT) array to control each pixel, resulting in better performance and image quality.
Differences between PMOLED and AMOLED
The main differences between PMOLED and AMOLED displays lie in their control mechanisms and applications. AMOLED displays are favored for high-end devices due to their superior quality, while PMOLED is used in simpler applications.

Advantages of OLED Displays
Superior Image Quality
OLED displays provide vibrant colors, deep blacks, and high contrast ratios. Each pixel emits light independently, allowing for true black levels and a dynamic range that surpasses traditional LCDs.
Flexibility and Thinnes
OLEDs are incredibly thin and flexible, making them ideal for innovative designs such as foldable smartphones and curved displays. This flexibility also opens up possibilities for new form factors in various devices.
Energy Efficiency
OLED technology is more energy-efficient than traditional displays because it doesn’t require backlighting. This efficiency translates to a longer battery life for portable devices.
Faster Response Times
With faster response times than LCD, OLED displays excel in fast-moving visuals, making them perfect for gaming and video playback.
Disadvantages of OLED Displays
Lifespan and Screen Burn-In
One of the main drawbacks of OLED technology is the potential for screen burn-in, where static images can leave permanent marks on the display. Additionally, OLEDs have a limited lifespan compared to other display technologies.
Cost Considerations
Producing OLED displays is more expensive due to the complexity of the materials and manufacturing processes involved. This higher cost is reflected in the price of OLED-equipped devices.
Susceptibility to Water Damage
OLED displays are sensitive to moisture, which can damage the organic materials. As a result, devices with OLED screens require effective sealing and protection against water exposure.
Working of an OLED Display?
An OLED display does not require many layers to form an image. You are free from the backlight layer, the bottom polarizer layer, and liquid crystal layers that form a thin and lighter display.
The OLED display is made up of organic chemical layers that are capable of producing light. They directly connected from the top to the bottom to the electrode layers. A polarizer layer that is added to the top of pixel layer the allows the light to pass through uniformly, and it also stops the interference of the reflection from the outside light.
What is an AMOLED Display?
AMOLED stands for Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. It is a type of OLED display that combines the benefits of OLED technology with an active matrix of thin-film transistors (TFTs) to control each pixel individually. This setup allows AMOLED displays to offer high performance, making them popular in smartphones, tablets, and other electronic devices.
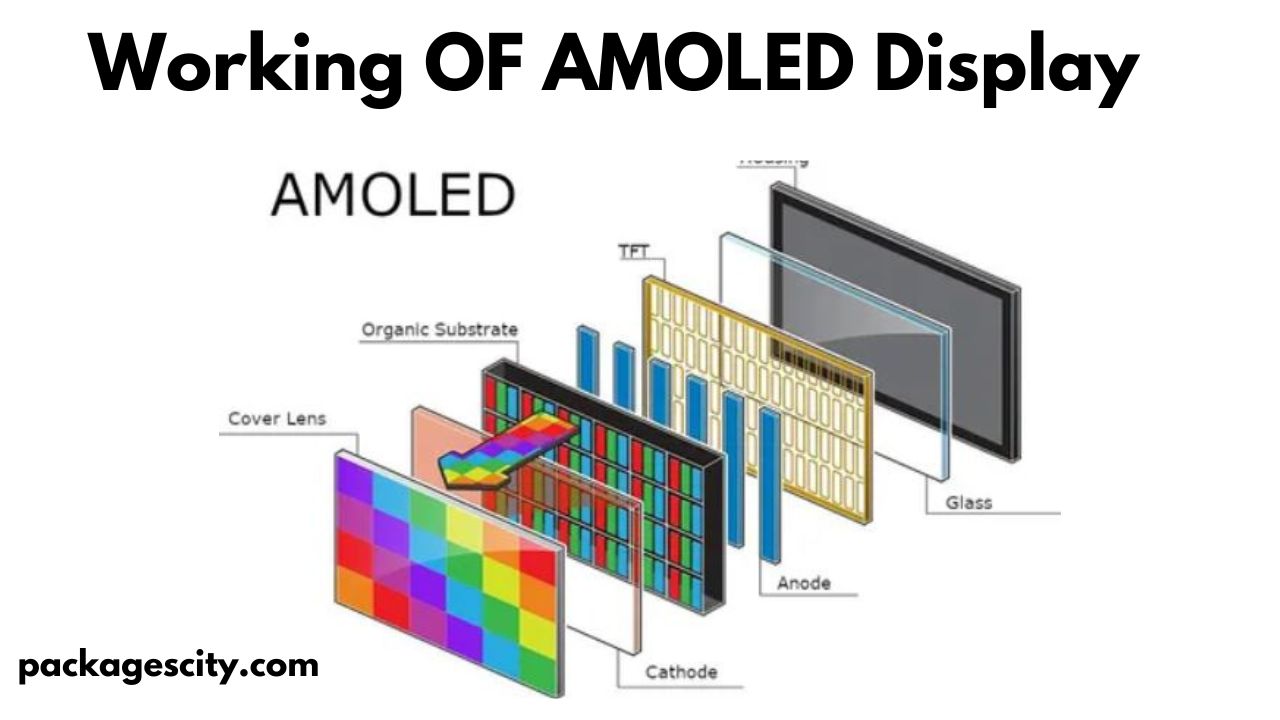
How AMOLED Displays Work
Active-Matrix Structure :The “active matrix” in AMOLED refers to the use of a matrix of TFTs to control the pixels on the screen. Unlike passive-matrix OLED (PMOLED) displays, which control rows and columns sequentially, AMOLED displays use a grid of transistors that actively manage each pixel. This active matrix allows for better control, faster refresh rates, and higher resolutions.
Electric Current: AMOLED displays operate by applying an electric current to the organic layers of the screen. Each pixel contains its transistor and capacitor, allowing precise control over the brightness and color of that pixel.
Light Emission: When an electric current passes through the organic compounds in the emissive layer, they emit light. This light can be red, green, or blue, depending on the specific organic materials used. By varying the intensity of these colors, AMOLED displays can produce a full range of colors.
Pixel Control: Each pixel’s brightness and color are controlled individually by its dedicated transistor, which allows for precise and dynamic color representation.
Advantages of AMOLED Displays
High Contrast Ratios
AMOLED displays are known for their high contrast ratios because each pixel emits its light. When a pixel is off, it is completely black, creating deep blacks and enhancing the overall contrast of the display.
Vivid Colors and High Brightness
The ability to control each pixel individually allows AMOLED displays to produce very vibrant and accurate colors. Additionally, AMOLED screens can achieve high levels of brightness, making them readable even in direct sunlight.
Wide Viewing Angles
AMOLED displays maintain consistent color and brightness levels from wide viewing angles. This is due to the lack of a backlight and the way light is emitted directly from the pixels.
Thin and Flexible Design
Because AMOLED displays do not require a separate backlight, they can be made thinner and more flexible than other display technologies. This flexibility has enabled the creation of curved and foldable screens.
Energy Efficiency
AMOLED displays are more energy-efficient, particularly when displaying darker images because individual pixels can be turned off completely. This means less power is used compared to LCDs, which rely on a constant backlight.
4. Disadvantages of AMOLED Displays
Burn-In Issues
One of the main drawbacks of AMOLED technology is burn-in, where static images or prolonged display of certain elements can leave a permanent mark on the screen. This occurs due to uneven wear of the organic materials.
Cost
AMOLED displays tend to be more expensive to produce than traditional LCDs or even other types of OLED displays. This higher cost can be a factor in the pricing of devices that use AMOLED screens.
Lifespan
The organic materials used in AMOLED displays can degrade over time, potentially leading to reduced brightness and color accuracy as the screen ages.
What is SAMOLED
Ongoing advancements in AMOLED technology aim to address its limitations and enhance its capabilities. Research is focused on improving durability, reducing burn-in issues, and making production more cost-effective. The future of AMOLED technology looks promising, with potential applications expanding into new and innovative areas.
This is a technology that I used by the Samsung company in their smartphone display. In the SAMOLED display, there are no differences in the technology of the display, The use and the architecture are the same as the AMOLED display. SAMOLED stands for Super Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. It is a variation of OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology, enhanced to provide better performance and image quality.
A SAMOLED display is composed of multiple layers, including the organic light-emitting layers, an active matrix layer for controlling pixels, and protective layers to enhance durability and longevity.
OLED Gives You Better Contrast Ratio
From the technician’s point of view, the contrast of the display is the ability that show the whitest white and the deepest dark color on the screen. It also gives the intensity difference in the two colors of the display side by side. The higher the difference the better that has the contrast ratio and gives you the image quality.
OLED displays do not need a backlight in their display. And they do not have any suffering issues like light bleeding. The Light bleed is common in the entry-level LCDs where you should notice the fading slightly of the color at the corner or edge of the screen. The most important and noticeable point is that the display shows the image in more deeper color.

The OLED display pixels are their own generating light and are capable of switching off individual pixels when they are not in use. This allows them to display the true deep black color or shade in the image.
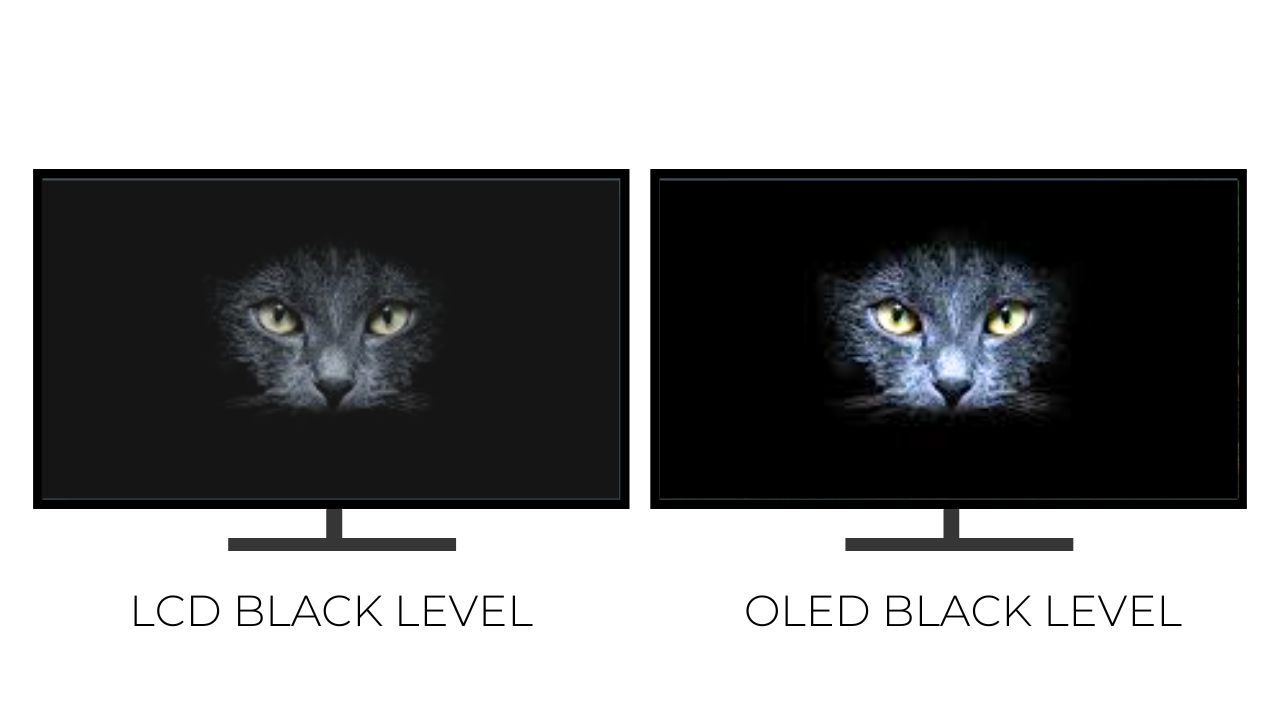

The Liquid layers are not capable that are blocking all the light that is passing through when they are showing the black color. Now some latest LCDs use a technique called local dimming to counter the issue of the light bleed. Where the LED is used the blacklight can be switched off when the pixels are in the black.
Better Viewing Angle in OLED
The LCD monitors and the TV screen in the beginning of the years suffered an issue that is a lot that the color on the display that is appeared a faded shade when you are view from the outside at a 120-degree angle of the display.
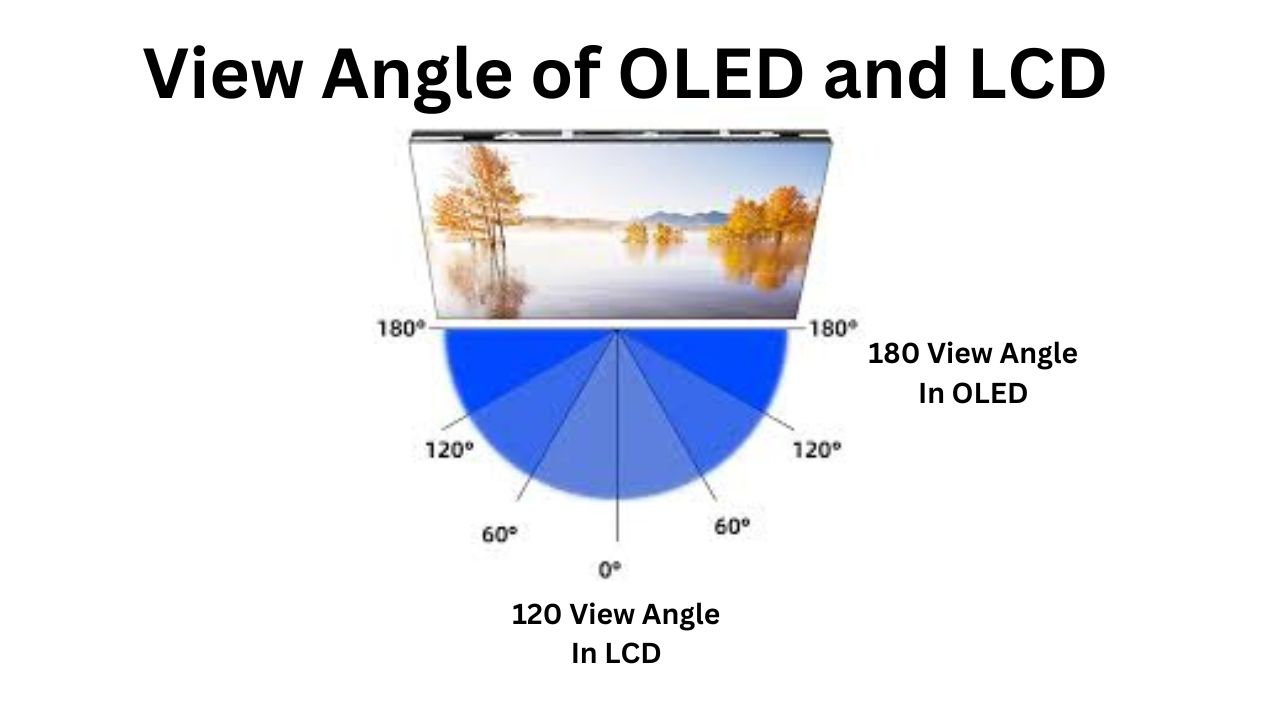
This happens when the multiple layers that are polarized the most allow the light to be emitted into a straight line. The OLED Does not suffer the limitation of the view angle their angle is almost 180 degrees.
In recent years LCDs have the significant improvement in their viewing angle. The LCD has a display with IPS capability that uses the improved arrangement of the pixels that increase the contrast of the color-producing ability of the display. It improves the viewing angle. The LCD has a low refresh rate and has an average display.
Conclusion
Choosing between OLED, AMOLED, and LCD display comes down to understanding your needs and preferences. OLED and AMOLED screen are known for their stunning color accuracy, deep blacks, and quick response times. They offer a superior viewing experience with high contrast and the display is energy efficiency. However, they can be more expensive and might suffer from screen burn-in over time.
In contrast, LCD displays, including those with LED backlighting, are usually more affordable and don’t have the risk of burn-in. They use a backlight to illuminate pixels, which can result in less vibrant colors and lower contrast compared to OLED and AMOLED. Even that the LCD technology has come a long way and it continues to be a solid option for many people.
If you want top-notch color and contrast and don’t mind spending a bit more, OLED or AMOLED might be the way to go. But if you’re looking for something more budget-friendly and reliable, an LCD display could be your best bet. Understanding these differences helps you pick the display that fits your lifestyle and budget perfectly.
